 In my last post comparing writing programming and writing fiction, I concluded both were similar because of their relationship with their practitioners. “Art is a kind of recruiting poster for itself,” I wrote. “An art attracts its own artists.”
In my last post comparing writing programming and writing fiction, I concluded both were similar because of their relationship with their practitioners. “Art is a kind of recruiting poster for itself,” I wrote. “An art attracts its own artists.”
Wait—is computer programming art? It’s accepted to call fiction art, but can computer programming really be considered
the conscious use of the imagination in the production of objects intended to be contemplated or appreciated as beautiful, as in the arrangement of forms, sounds, or words. (The Free Dictionary)
Think of what programming a computer really boils down to: Ordering and organizing a series of mathematical instructions followed precisely by the machine. The computer is allowed no imagination in its interpretation of those instructions (if it possessed an imagination, which it doesn’t, at least not today). If there’s an art in computer programming, it stands in the purview of the programmer, not the machine. That’s how it should be. The art of painting is not in the tubes or cans of paint, but in the painter.
But is the arrangement of those computer instructions somehow “beautiful”?
It’s important to discern a difference between a computer program being art and the act of programming as an artistic form. Let’s start with the latter.
I believe programming is an art form, at least by modern notions of the term. Writing fiction and writing code requires continuous subjective decision-making during the entire process (a “conscious use of the imagination”). A personal fervor is vital for quality results. When a writer lacks that fervor, it shows in the end result, both for fiction and computer programs.
Programming is not a rote process of memorization and recall. There is no “correct” way to write a computer program but, like writing a novel or a short story, there are many wrong ways.
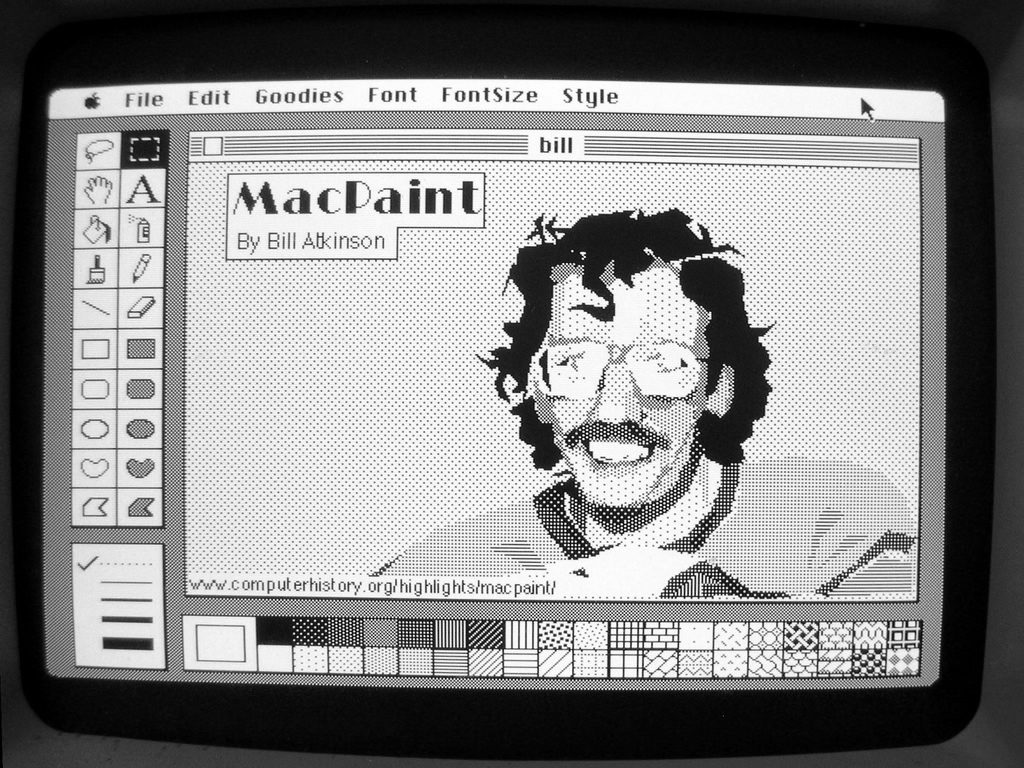
Bill Atkinson, creator of the original MacPaint, painted in MacPaint. (Daniel Rehn, CC BY 2.0)
Coding requires taste, aesthetics, and an eye for detail. Programmers develop deeply personal philosophies. Some coders prefer verbosity (like Henry James in his later years) while others prefer economy (like Hemingway or Cain’s early work).
There’s a scene in August Wilson’s Fences that is one of the most distilled scenes I’ve ever read: The father and son debate buying a TV to watch the World Series. On the surface a mundane domestic moment, the scene is actually Fences in-miniature. The beauty of this scene mirrors brilliant software design, where each piece of the program is intimately connected to the entire application.
Years ago, I could always tell when I was working with a programmer who started coding on the Macintosh versus a programmer weaned on Microsoft Windows—the two companies have distinct programming styles and philosophies. Programmers who learned to code on those operating systems carried those styles and philosophies with them to other platforms and projects.
A computer program can be functional, operating, and seemingly free of bugs, and a programmer may still read the code and say it doesn’t “look” right. (The trendy term for this is “code smell.”) What’s more, two programmers may say a program doesn’t “look” right for entirely different reasons. This reminds me a great deal of the world of poetry, where poets may agree a poem is poorly executed and then squabble over the reasons why. (There are similar disagreements in the world of fiction, but I find them to be less…doctrinaire.)
Writing and programming both involve elements of discovery and improvisation. Even though I’m writing a series of blog posts advocating outlining stories before writing them, I don’t believe an outline can—or should—contain every detail present in the final story. An outline should not be so rigid as to prohibit discovery during the writing process.
For a long time, there was a big push to eliminate discovery and improvisation in the world of software development, as “discovery” and “improvisation” seem undesirable in a field of proper engineering. (In the 1960s, IBM famously discovered that the number of bugs a programmer produced was proportional to the amount of code he or she wrote. Their solution: limit the lines of code a programmer could write per day, a logic straight from the pages of Catch-22.) Newer software philosophies, notably Extreme Programming and Agile development practices, have flipped that thinking and embraced discovery and improvisation as healthy and necessary.
Suspicion of programming as an art form probably springs from a general lack of understanding of how programs are written. Programmers share an arcane terminology among themselves. They build and manipulate mysterious machines that have come to play a powerful, sometimes menacing, role in our lives.
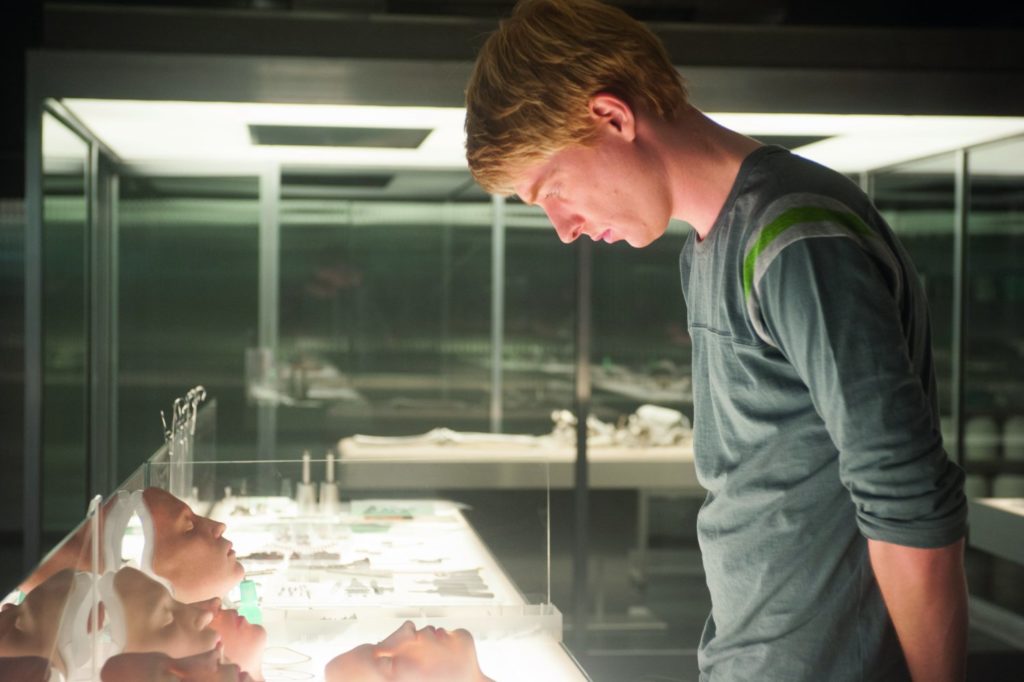

Ex Machina, a 2015 film about a computer programmer who falls in love with an artificially intelligent android.
That suspicion probably also arises from stereotypes. Programmers don’t look like artists. In popular culture, programmers are portrayed as geeks more comfortable around machines than humans. Sometimes coders in film or TV even fall in romantic love with their own programs. (Never mind that this trope originated in antiquity and regards an artist and not a bricklayer or farmer or soldier.)
Another reason people question programming as an art is that computer programs “do” things. There’s an academic suspicion of pure art having any sort of utility, probably due to fears of commodification and commercialization. We don’t think of Vermeer’s Girl with a Pearl Earring as “doing” anything other than hanging on a wall in some drafty museum, but it must be doing something to cause people to stand in line for hours to view it. It’s funny, this idea that pure art doesn’t “do” anything when it so plainly does. If art didn’t do anything, why would we care about it?
And this rolls back to the distinction I made earlier: Is computer software itself art? I’ll challenge the question with a question in return. We regard skyscrapers and bridges and automobiles and colanders as kinds of art. We laud architects, automotive designers, and commercial illustrators as artists. Why treat computer programs and their creators differently?
Next: Iterative processes








 Late last year I wrote about
Late last year I wrote about 



 Then comes the title page, a clean, almost retro layout befitting the book’s original publication in the 1940s. A small note indicates the final chapter was written more recently, forty years after the bombing of Hiroshima. Again, that’s a nice piece of information to have—that while I’m reading a history book originally published contemporaneously with the events it describes, it’s not been frozen in time.
Then comes the title page, a clean, almost retro layout befitting the book’s original publication in the 1940s. A small note indicates the final chapter was written more recently, forty years after the bombing of Hiroshima. Again, that’s a nice piece of information to have—that while I’m reading a history book originally published contemporaneously with the events it describes, it’s not been frozen in time.